Plant-based proteins have become extremely popular in recent years as an alternative to animal proteins. Whether you're a vegan, vegetarian, flexitarian, or simply want to reduce your meat consumption, plant-based proteins offer a healthy and sustainable option. Below we discuss the benefits of plant-based proteins, the different sources, and how they can benefit both your health and the environment.
What are vegetable proteins?
Proteins are essential nutrients needed for building muscle, producing hormones, and supporting various bodily functions. Traditionally, many people get their proteins from animal products such as meat, fish, dairy and eggs. Plant proteins, however, come from plant sources such as legumes, nuts, seeds, grains, and some vegetables. They provide a complete amino acid profile (essential building blocks of proteins) when combined properly.Health benefits
Plant proteins may offer a number of health benefits over animal proteins. Many plant-based protein sources are rich in fiber, antioxidants, and essential micronutrients such as magnesium and iron. Unlike many animal products, plant-based sources often contain fewer saturated fats and no cholesterol, which can contribute to a lower risk of cardiovascular disease. Additionally, eating more plant-based foods has been linked to a lower risk of chronic diseases such as type 2 diabetes, certain cancers, and obesity.
Another important advantage is that vegetable proteins are generally easier to digest. People who have difficulty digesting heavy animal products may benefit from switching to plant-based alternatives.
Sustainability and environmental impacts
One of the biggest reasons plant-based proteins are gaining popularity is their much smaller carbon footprint compared to animal proteins. Livestock farming is one of the largest contributors to greenhouse gas emissions, deforestation, and water pollution. Growing plants for consumption requires much less water, land, and energy than raising animals. According to studies, switching to a plant-based diet can reduce your personal carbon footprint by up to 50%. This makes plant proteins a crucial component in the fight against climate change.
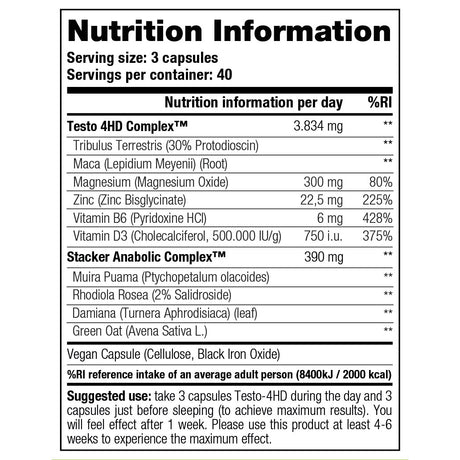
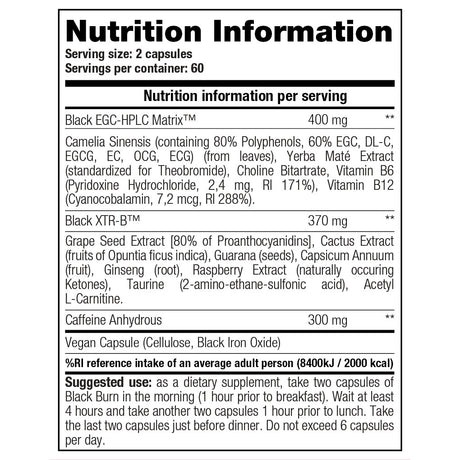
Vegan sports nutrition products from Stacker 2
View our 100% Plant-Based Protein from Stacker 2 here.
View our new Barbarian Vegan Protein Bar here.
View all Vegan products from Stackeronline here.
Popular sources of vegetable protein
There are numerous sources of plant-based protein that can easily be added to your diet. Here are some of the most popular:
- Legumes: Lentils, chickpeas, beans and peas are rich in protein and fiber.
- Soy: Soy products such as tofu, tempeh, and edamame contain complete proteins, meaning they contain all the essential amino acids.
- Quinoa: This seed is often considered a “superfood” due to its high protein content and complete amino acid profile.
- Nuts and seeds: Almonds, chia seeds, hemp seeds and sunflower seeds are excellent sources of both protein and healthy fats.
- Grains: Whole grains such as oats and farro provide a good amount of protein and fiber.
Vegetable proteins in the sports world
For athletes and bodybuilders who are used to animal proteins such as whey, vegetable proteins can be an excellent alternative. Protein powders made from peas, brown rice and hemp provide high concentrations of protein and are easily digestible. They help with muscle recovery and building, without the side effects of dairy or animal products.
Conclusion
The shift to plant-based proteins is not only good for your health, but also contributes to a more sustainable future for our planet. By choosing plant-based sources of protein more often, you can enjoy a healthy, varied diet that is rich in essential nutrients. With the growing availability of plant-based products, from meat substitutes to protein powders, it is now easier to replace animal protein without sacrificing taste or nutrition.