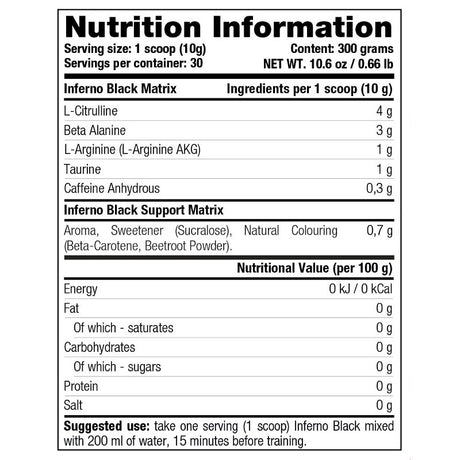
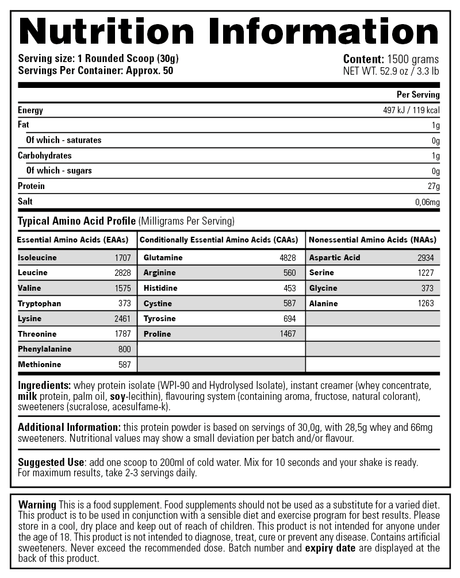
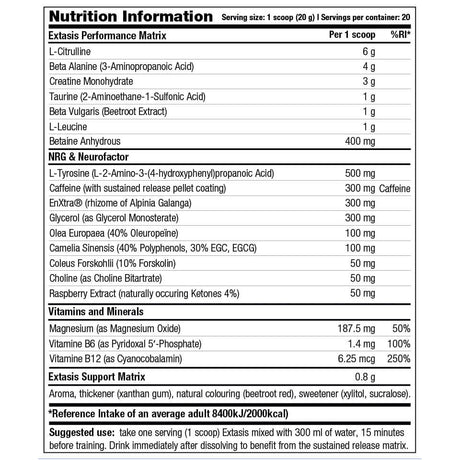
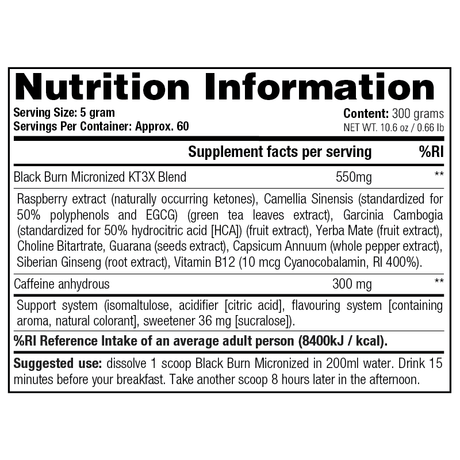
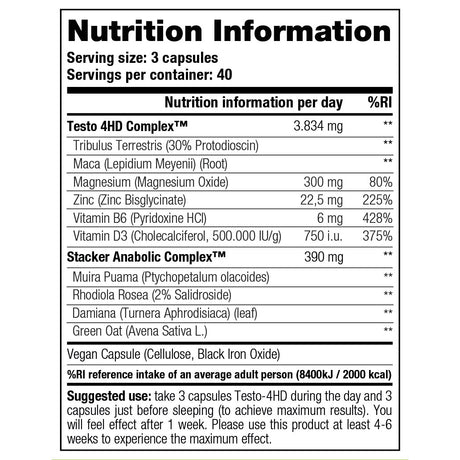
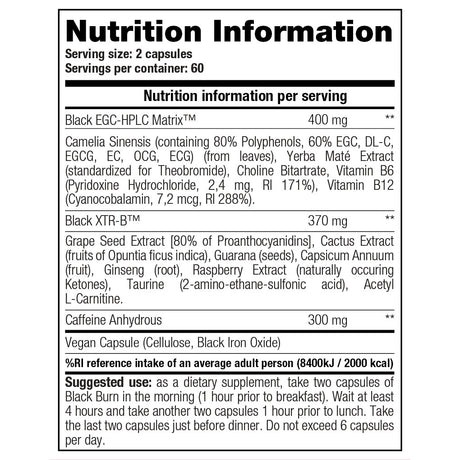
Creatine is a supplement that you often encounter in the (strength) sports world because it plays an important role in supplying energy to muscle and nerve cells. Many people do not know that the body produces 1 to 2 grams of creatine every day from three amino acids: arginine, glycine and methionine. The substance is produced in the kidneys and liver, after which it is stored in our muscles. Our daily diet also ensures the production of creatine and is mainly obtained through (red) meat and fish.
About two-thirds of this consists of creatine phosphate and the rest of free creatine. Creatine phosphate is an energy source that your body uses for high-intensity exercise. The benefit of creatine therefore also varies greatly per type of effort or training. The supplement mainly supports training at high or maximum intensity and can help increase strength and muscle mass, helping you achieve your training goals faster. That is why it is so popular among strength athletes.
Training intensity
The greatest performance gain is with maximum efforts that last a maximum of 30 seconds, but you can benefit from it for up to 150 seconds. So the effect is greatest with short explosive movements. Think of short sprints and explosive strength exercises in the gym. Creatine can also improve performance in team competitions where short sprints are often made.
Taking creatine is less useful in endurance sports, because body weight can increase due to water retention. Those extra pounds are often not desired. However, extra creatine in the body can ensure a more powerful final sprint during an endurance run, for example. It is good to list the pros and cons for yourself before you start supplementing.
Dosage
To benefit from creatine faster, you can start with a loading phase. For example, take 5 grams of creatine 4 times for 5 to 7 days and then reduce the dose by 3-5 grams. This is how you build up a creatine supply. However, there is no point in taking more creatine than the recommended amount. The moment of taking it is also not very important. As long as you plan it around your training moments.
Creatine suitable for vegetarians and vegans
Stacker has 2 creatine products in its range both of which are also suitable for vegetarians and vegans. Athletes on this diet get less creatine from their diet because it mainly occurs in meat and fish. That is why these people can sometimes benefit even more from supplementing with creatine supplementation.